Binance futures: the complete guide
Binance futures allow you to trade in cryptos with a leverage effect: this means that both your potential gains and losses increase. In this guide, we will explain how Binance futures works and discuss whether this is a good option for investors.
10% permanent discount on futures trading
We would like to give you a present: when you open an account on the futures platform, we share our friend discount with you! You will receive a permanent 10% discount on all your transaction fees, which can be a real money saver, especially for active traders. Use the button below to open an account with Binance futures right away:
You can still use this option if you already have a Binance Spot account. Binance futures is a separate program from the normal Binance spot trading.
How to open a Binance futures account?
- Visit the Binance website by clicking here
- Open an account with an e-mail and password
- Click on open an account
- Verify your email address
- Navigate to derivatives and USD(S)-M futures
- Click on the open futures button to open your account
What are futures?
Before we explain how Binance futures work, this guide will briefly discuss what futures actually are.
A future allows you to speculate on the price development of an underlying asset. A future obliges you to deliver the underlying asset at a certain time at a certain price. A future consists of:
- Exercise price: the price at which you promise to buy or sell the underlying asset.
- Expiry date: the date for which delivery is required.
Futures can also differ greatly in their terms. Futures can differ in the leverage you can apply and the interest charges. You should therefore always carefully research the characteristics of the future you wish to invest in on Binance!
What can you use Binance futures for?
You can use Binance futures within your investment strategy:
- Hedge: a future allows you to hedge against risks, as you can lock in the price you receive for an asset such as Bitcoin.
- Leverage: with Binance futures, you can use up to 125X leverage. Your profits and losses will then increase faster.
- Short position: you can also use Binance futures to speculate on a falling price of a crypto.
What happens after the expiry date?
You can settle a future in two ways:
- Physical delivery: the underlying crypto is actually delivered.
- Cash settlement: you receive the profit or loss on the position in your account.
On the expiry date, you can also extend the contract. These are the possibilities:
- Offsetting: you can close a future position before it expires by opening an opposite position of the same size.
- Rollover: you open a new position at the end of the expiry date, as a result of which the expiry date shifts to the future.
- Settlement: you close the position and settle it by physical / cash settlement.
How can you add money to your Binance futures account?
Your Binance futures account has a separate wallet. You can move money from your normal Binance wallet to your futures wallet at any time.
Haven’t added money to your Binance account yet? Click here to read our guide on depositing money & crypto on Binance.
If you want to add money to your Binance account, you can press the transfer button within your Binance futures account.
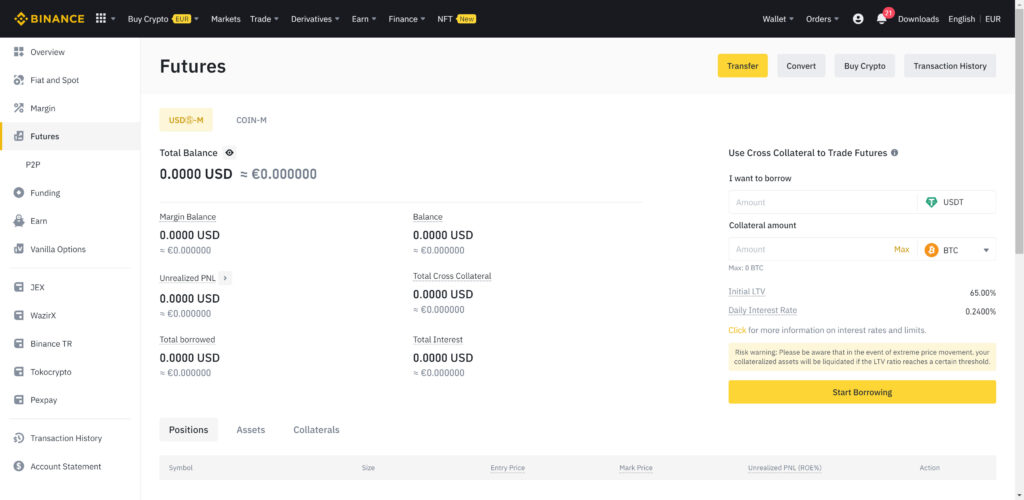
Then enter the amount you wish to add to your Binance futures account and press confirm.

The Binance futures interface
Binance offers an enormous amount of trading possibilities, and this number is even more extensive with Binance futures. In this manual, we will help you get started so you can open your first futures position.
Do not worry: in this article, we cover everything you need to know, step by step. If you still have questions, you can leave a comment below this article.
In the menu, you can first indicate which type of future you want to trade: here you can choose between USDⓈ-M and COIN-M. The main difference is that with USDⓈ-M you use the stablecoin USDT as collateral, and with COIN-M you use the cryptocurrency itself. Later on in the article, we will explain the differences in more detail.
You also have to indicate in the menu whether you would like to trade a future with a fixed delivery date or with a perpetual delivery time. Futures with a perpetual delivery time do not expire, so there is no particular moment at which you are obliged to deliver.

On the left-hand side of the screen, you will see the details of the future you wish to trade. You can select a pair in which you want to trade from the selection menu.
In this example, we trade a perpetual BTCUSDT future. After clicking on a future pair, you will see the order summary on the right-hand side of the screen, where you can enter the data for your first future position!
Leverage and margin explanation
You can use leverage with futures. When you use leverage, you only put in part of the money required for the position. You borrow the remaining part of the position from Binance.
By using leverage, your profits can increase. Cryptos are already very volatile and with Binance, you can increase this volatility by a factor of 125 with futures. If you speculate on a rising Bitcoin price with a leverage of 125 and the price rises by 10%, your actual profit is 1250%! This works in both directions: you will also lose a substantial amount of money much quicker.
The margin
Binance does not give you this trading opportunity without collateral. Depending on the type of future you choose, you will be required to deposit either a cryptocurrency (COIN-M futures) or a stablecoin (USDⓈ-M).
The leverage determines the required initial margin. When you apply a leverage of 1:20, you have to put in at least 5% of the amount yourself. Let’s see what happens when you want to open a position for $1000:
- COIN-M: you then need $50 worth of the underlying crypto.
- USD-M: you then need $50 worth of the underlying stablecoin
After you have opened the position, you do not need to keep this initial margin. However, there is always a maintenance margin. This is the amount of collateral that must always be present in your account to keep the positions open. These percentages may fluctuate, but are in any case considerably lower than the initial margin. At the time of writing, the maintenance margin for a leverage of up to 20 is only 1% of the position.
Beware of liquidation!
Your position is liquidated when the value of your collateral falls below the maintenance margin. This is also called a margin call.
With a leverage of 1:20, the price only has to fall by 4% before you can face liquidation. Remember, you are only putting in 5%, so you will quickly reach the 1% maintenance margin. You can avoid liquidation by closing the position or by depositing more collateral.
What does the leverage do to your result?
A leverage of 1:20 has a considerable impact on your results! An increase of 5% already doubles your deposit. 5% X 20 is in fact 100%! However, you still have to consider the costs for calculating your exact return.
Of course, this works in both directions: if the price falls by 5%, you lose your entire deposit. If you open multiple positions on Binance futures, the failure of one position can also result in you losing all your trading positions. You should therefore be well aware of the enormous risks of Binance futures!
You can avoid the risk of one position jeopardizing all your positions by using isolated margin. With isolated margin, you indicate which part of the margin you want to use for each separate position.
Long or short
You have two options on Binance: you can open a long or short position. When you open an order, you simply decide whether to go long or short by pressing the appropriate button.

- With a long position, you speculate on a rising price.
- With a short position, you speculate on a falling price.
If you want to open a position on BTCUSDT, you will use a short position to speculate on a fall in Bitcoin’s value in relation to the US dollar.
Types of orders
At Binance, you can choose from various order types. In this part of the Binance futures tutorial, we will discuss these order types.
Market order
With a market order, you open the position immediately at the best available price. This has the advantage that you know for sure that the position will be opened. A disadvantage of a market order is that the price may turn out to be less favourable than expected.
Limit order
With a limit order, you open the position at a set price. This has the advantage that you never pay more or receive less than expected. At the same time, the disadvantage is that your position is not always opened.
Market limit order
With a market limit order, a position immediately closes when a certain trigger price hits. This allows you to manage your positions when you are not in front of your computer.
Stop limit order
With a stop limit order, you can automatically close a position at a certain loss. The difference with a market stop order is that with a stop limit order you have more control over the price you receive/pay.
In this manual, we explain in more detail how a stop limit order works.
Take profit market/limit order
This type of order works the same as the stop order, but intents to close your position at a certain profit.
Trailing stop order
A trailing stop order moves automatically with the price of the crypto. You can use a trailing stop to maximize your profits and protect your position from adverse developments at the same time.
You place a trailing stop order a certain percentage below (long position) or above (short position) your trading position. The trailing stop level then moves with the price development when it moves in the favourable direction.
The activation price is the price at which the trailing stop order activates. The callback rate is the percentage at which the price movement is subsequently followed.
Mark versus last price
The last price indicates the last price at which the contract traded. This value is also used to calculate your profit/loss on open positions.
The mark price is established by combining data from multiple exchanges and should prevent market manipulation.
When you open an order, you can decide what type of price to use.
Additional settings for limit orders
- Post-only: the order is first added to the order book, so you always pay the maker fee.
- TIF: specify how long the order will remain active, choosing from:
- GTC (Good Till Cancel): the order remains active until it is cancelled or fully executed.
- IOC (Immediate or Cancel): the order is executed immediately. The part that is not executed immediately is cancelled.
- FOK (Fill or Kill): The order must be executed immediately. If this is not possible, it will be cancelled.
Be mindful of future fees
When you start investing in futures on Binance, it is important to keep a close eye on the costs. After all, costs decrease your return, and it is therefore important to limit them.
Transaction costs
You pay transaction costs on Binance when you open a position. Compared to the competition, these costs are lower on Binance than at many other exchanges. However, the costs may turn out to be higher than you initially expect: this is because the transaction costs multiply by the applied leverage.
If the transaction costs are 0.02%, this does not seem too bad. With a leverage of 20, however, the costs are 0.4%: still not bad, but a lot higher than the normal spot transaction costs of 0.1% on Binance. You can read more about the costs of Binance in this article.
Funding rate
It is also essential to pay attention to the funding rate. The interest rate is 0.03% daily (0.01% per funding interval). Only for pairs with BNB, this interest rate is 0%. Depending on the pair, a premium is also calculated on top of this.
The funding rate can be either positive or negative. The long or short position holders pay this fee to the counterparty. When the funding rate is positive, the long holders pay it to the short holders. When the funding rate is negative, the short holders pay it to the long holders.
Keep a close eye on the funding rate, as you can easily pay more than 10% on an annual basis. This can put a lot of pressure on your return. Futures are therefore predominantly suitable for short-term investments.
Binance does not earn anything on the funding rate: this amount exchanges between users. Remember that you pay this rate over the full amount, not just on the margin!
What type of futures can you trade in?
You can trade USD-M and COIN-M futures on Binance. In this section of the manual, we will explain the differences.
What are USDⓈ-margined futures?
USDⓈ-margined display in BUSD or USDT. USDT is a stablecoin: this means that the value of 1USDT is equal to the value of 1 US dollar. As a result, USDⓈ-margined futures are more transparent, and it is easier to calculate your profit or loss.
An advantage of USDⓈ-margined futures is that you don’t have to different cryptos to open positions. After all, you can use USDT for all your future trading positions, which means that you can save money on transaction fees.
Nevertheless, many crypto fanatics do not choose USDⓈ-margined futures. After all, you need to hold a lot of collateral to trade in futures. USDT is equal to the dollar exchange rate, which means that this part of your assets will not rise when the crypto markets are performing well.
USDⓈ-margined exist without an expiry date (perpetual) and with an expiry date per quarter (quarterly).
What are COIN-margined contracts?
COIN-margined contracts use crypto assets as collateral, which can make this type of future more complicated. For example, one BTC future represents $100, while one Ethereum contract represents $10.
With COIN-Margined contracts, you do not need stablecoins. COIN-Margined contracts are not available without expiry date (perpetual), but are available quarterly and half-yearly.
COIN-margined contracts are interesting for long-term investors. The contracts are paid out in the investor’s own crypto, which means that if you buy a future contract on Bitcoin, you will receive more Bitcoin. However, you must be extra careful: the crypto that serves as collateral is very volatile, which means that you can be confronted with a margin call sooner.
In addition, your payouts are not linear; this is normal with this type of inverse future contact.
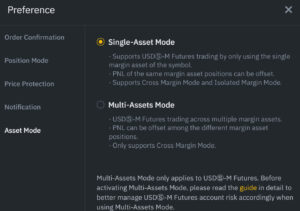
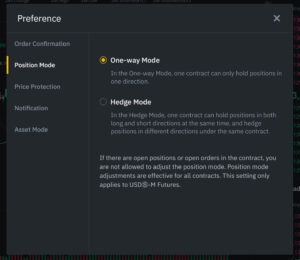
Using Hedge Mode
At Binance, it is also possible to hold both long and short positions at the same time for the same contract. This helps you to respond to small, interim movements and hold the other position for the longer term. However, you will have to adjust the settings. By default, Binance will automatically close the old position when you open a position in the opposite direction.
You can enable hedge mode by:
- Click on preference in the top right of the screen.
- Navigate to Position Mode and click on Hedge Mode
Conclusion Binance futures
With Binance futures, you can achieve a very high price return in a short period. However, it is important to remember that Binance futures are extremely risky: crypto is already very volatile in itself, and futures increase this even more.
Binance futures are therefore not suitable for novice crypto investors. Do you have little experience with investing in crypto? Then first read the Binance manual to learn how buying and selling normal cryptos works.
Frequently asked questions about Binance futures
This depends on the type of future you are buying. Perpetual futures have no expiry date, which means you can hold them indefinitely. Some futures have a fixed date on which they expire: this happens, for example, once every quarter. Your results are settled at the end of the period.
5X indicates the leverage on Binance. If it says 5X, this means you are using a leverage of one to five. You then contribute 20% of the position yourself, while the rest is financed. This means that both your profit and loss increase five times as fast.
According to the majority of Islamic scholars, trading on margin is haram. This is because when you use futures, you pay interest and that is not allowed according to Islamic teaching.
The costs of trading Binance futures can add up quickly. You pay a fee for each transaction. These costs are calculated on the full amount (i.e. after you have applied the leverage). There may also be a charge for funding the position: this is also known as the funding rate.
To avoid liquidating your positions, make sure your Maintenance Margin is not broken. If your Maintenance Margin is 1%, you must always hold at least 1% of the total amount of the position as collateral. If your collateral no longer covers the position, you may face liquidation. Your position will then automatically close with a loss.
Binance itself does not charge interest on futures, but it does calculate a funding rate. This funding rate is used to keep the price of a future in line with that of the underlying security. Depending on the market situation, investors who are long or short in the security receive this fee.
With margin trading, you can trade in pairs that are more exotic: think for instance of ADA/ETH or BTC/ETH. This allows you as a trader to speculate on the performance of two cryptocurrencies in relation to each other. In case of margin trading, however, the costs increase considerably over a longer period of time and the possibilities are more limited. Therefore futures are often more suitable for active speculation.


